Compass — Required Graph API Permissions
Understand every permission Compass needs and why, including the 4 administrative permissions that require admin consent.
Overview
Cloudiway Compass performs a comprehensive security audit of your Microsoft 365 environment. To do so, it requires a set of Microsoft Graph API application permissions granted via admin consent in your Azure AD / Entra ID tenant.
The vast majority of these permissions are read-only — Compass never modifies your data, users, or settings. However, 4 permissions are classified as administrative access by Microsoft because they provide elevated capabilities. This article explains in detail what each permission does, why Compass needs it, and what scanning features depend on it.
Permissions Summary
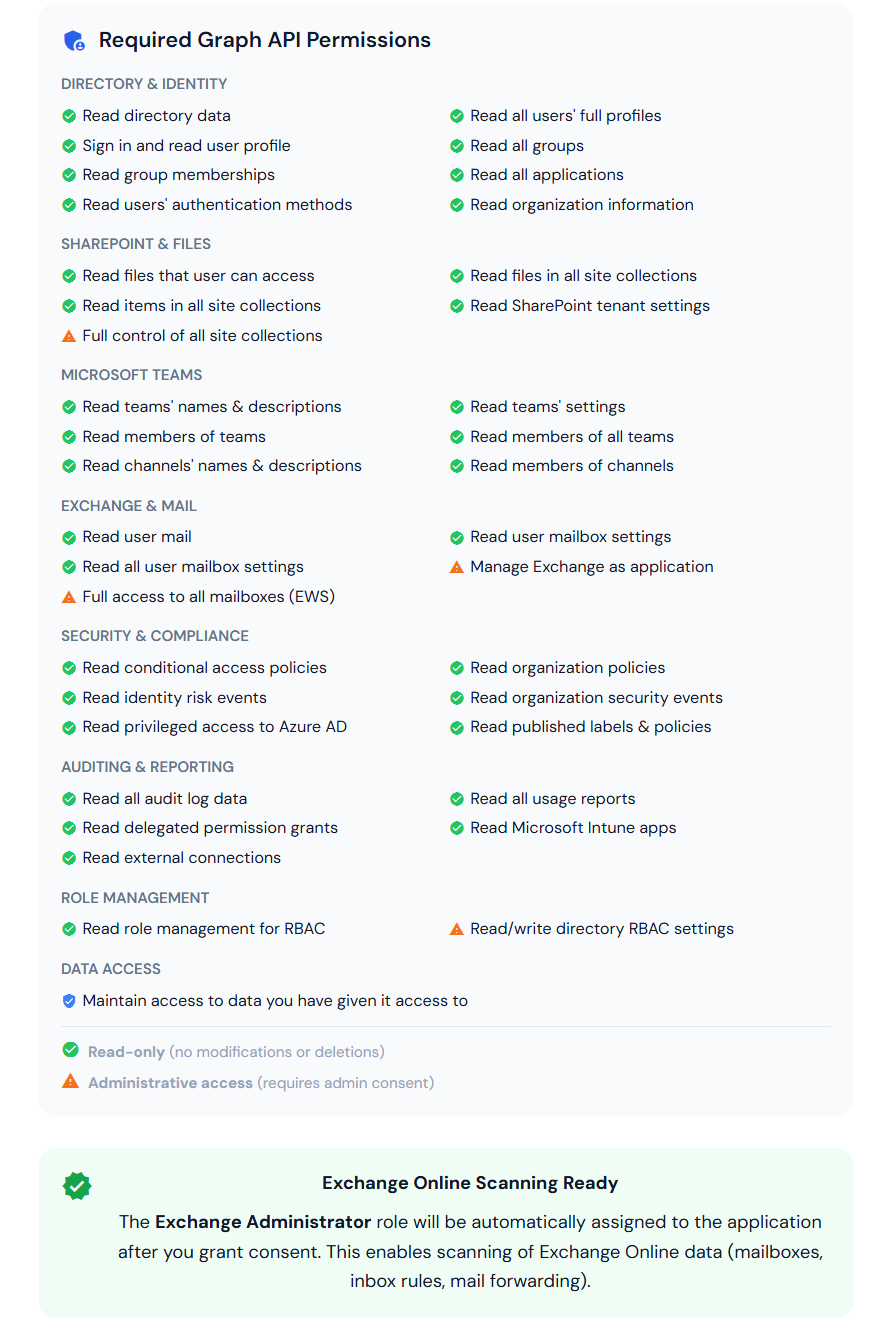
Click the image to view in full screen
Read-Only Permissions
The majority of permissions are read-only
Compass uses read-only permissions for most of its scanning capabilities. These permissions allow the application to read data from your Microsoft 365 environment without the ability to modify, create, or delete anything. This includes user profiles, groups, SharePoint sites, Teams, mailbox settings, security policies, audit logs, and reports.
What is scanned with read-only permissions?
- • User accounts, licenses, and sign-in activity
- • Groups, memberships, and ownership
- • SharePoint sites, sharing settings, and external access
- • OneDrive provisioning and sharing
- • Teams, channels, and membership
- • Conditional Access policies
- • Sensitivity labels and DLP policies
- • Security events and identity risks
- • Usage reports and audit logs
- • Application registrations and service principals
The 4 Administrative Permissions
Four permissions are classified by Microsoft as administrative access. They require explicit admin consent from a Global Administrator. Below is a detailed explanation of why each one is necessary and what happens if it is not granted.
| Permission | API Scope | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Full control of all site collections | Sites.FullControl.All | Read Restricted Content Discoverability (RCD/Copilot) settings |
| Full access to all mailboxes (EWS) | full_access_as_app | Read inbox rules, forwarding, and mailbox delegations |
| Manage Exchange as application | Exchange.ManageAsApp | Enable app-only Exchange PowerShell scanning |
| Read/write directory RBAC settings | RoleManagement.ReadWrite.Directory | Auto-assign required roles + scan admin role assignments |
1. Full Control of All Site Collections
Why is this needed?
This permission is required exclusively to read Restricted Content Discoverability (RCD) settings — the tenant-level configuration that controls which SharePoint sites Microsoft 365 Copilot is allowed to search and index.
These RCD settings are not available through the Microsoft Graph API. They can only be accessed via the SharePoint Admin REST API (/_api/SPO.Tenant), which requires Sites.FullControl.All to authenticate.
What Compass scans with this permission
- • RCD tenant-level setting — Whether Copilot search is restricted to selected sites or open to all
- • Allowed sites list — Which specific sites are in the Copilot search scope
- • Per-site search scope — Individual site
SearchScopeproperty (Disabled, Site-only, Tenant, etc.) - • Site owner delegation — Whether site owners can control their own discoverability settings
Least privilege approach
SharePointTenantSettings.Read.All via Graph API.The
Sites.FullControl.All permission is
only used when scanning RCD/Copilot readiness settings.
What happens if this permission is not granted?
Compass will be unable to scan Copilot readiness settings (RCD). The RCD section of the audit report will show as "unavailable". All other SharePoint scanning (sites, permissions, sharing settings) will continue to work normally.
2. Full Access to All Mailboxes (EWS)
Why is this needed?
This is an Exchange Web Services (EWS) permission that enables Compass to read mailbox configuration data in app-only mode (without a signed-in user). Despite the name, Compass uses this permission in read-only mode to inspect mailbox settings, rules, and delegations.
What Compass scans with this permission
- • Inbox rules — Detects forwarding rules, auto-delete rules, and redirect rules that could indicate data exfiltration
- • Mail forwarding — Identifies mailboxes with
ForwardingSMTPAddressorForwardingAddressset, especially to external domains - • Mailbox delegations — Discovers Send As, Send On Behalf, and Full Access delegations between users
- • Folder permissions — Checks calendar sharing settings and folder-level permissions
- • Shared mailboxes — Identifies shared mailbox configurations and access patterns
Why not just use Mail.Read?
Mail.Read allows reading mail content, but certain Exchange-specific configurations (transport rules, detailed mailbox delegations, forwarding settings) require EWS-level access. full_access_as_app is the Microsoft-recommended way for applications to access mailbox data without user interaction.
What happens if this permission is not granted?
Compass will be unable to scan inbox rules, mail forwarding configurations, and mailbox delegations. Exchange Online risks (forwarding to external domains, suspicious inbox rules) will not be detected in the audit.
3. Manage Exchange as Application
Why is this needed?
This permission is a prerequisite for app-only Exchange Online PowerShell access. It allows the application's service principal to authenticate with Exchange Online Management, which is required for scanning certain Exchange configurations that are not available through the Graph API.
Microsoft requires this permission in combination with the Exchange Administrator directory role. Without it, even if the role is assigned, the application cannot authenticate against Exchange Online Management endpoints.
What Compass scans with this permission
- • Transport rules — Organization-wide mail flow rules that route, modify, or block email
- • Retention policies — Email retention and deletion policies
- • Anti-spam & anti-phishing configuration — Protection policy settings
- • DLP policies (Exchange) — Data Loss Prevention rules applied to email
How this works together with the Exchange Administrator role
Exchange.ManageAsApp permission together enable app-only PowerShell access. See the Automatic Role Assignment section below.
What happens if this permission is not granted?
Compass will be unable to scan Exchange Online configurations via PowerShell. Transport rules, retention policies, and Exchange-level DLP policies will not be included in the audit. Graph API-based Exchange scanning (inbox rules, basic mailbox settings) will still work.
4. Read/Write Directory RBAC Settings
Why is this needed?
This permission serves a dual purpose: it enables both the automatic setup of required directory roles and the security audit of admin role assignments across your tenant.
Write: Auto-assign directory roles
After admin consent, Compass automatically assigns two directory roles to its own service principal:
- • Exchange Administrator — Required for Exchange Online app-only authentication
- • Compliance Administrator — Required for Security & Compliance Center access (DLP policies, sensitivity labels)
Read: Scan admin role assignments
Compass scans all directory role assignments to detect security risks:
- • AR-001 Global Admins without MFA
- • AR-002 Excessive Global Administrators
- • AR-003 Permanent privileged role assignments
- • AR-004 Inactive admin accounts
- • AR-005 Service accounts with admin roles
- • AR-006 Guest users with admin roles
Why not use RoleManagement.Read.All only?
RoleManagement.Read.All is sufficient for scanning admin roles, and Compass does request it as well. However, the ReadWrite variant is needed to assign the Exchange Administrator and Compliance Administrator roles to the application's own service principal. Without it, these roles would need to be manually assigned by a Global Administrator, adding friction to the onboarding process.
What happens if this permission is not granted?
Compass will be unable to automatically assign the Exchange Administrator and Compliance Administrator roles. These roles would need to be assigned manually. Additionally, admin role assignment scanning (AR-001 through AR-006 risk codes) may be limited.
Automatic Role Assignment
Roles Automatically Assigned After Admin Consent
When admin consent is granted, Compass automatically assigns these two directory roles to its own service principal in your tenant. This is a one-time operation that happens immediately after consent.
Global Administrator grants admin consent for the Compass application
Compass locates its own service principal in the customer's tenant
Compass assigns Exchange Administrator and Compliance Administrator roles via the RoleManagement.ReadWrite.Directory permission
Exchange Online scanning is now fully operational — no further manual configuration needed
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Cloudiway Compass modify any data in my Microsoft 365 tenant?
No. Compass operates in read-only mode. The only write operation is the one-time automatic assignment of Exchange Administrator and Compliance Administrator roles to the Compass service principal itself. It never modifies your users, groups, settings, mailboxes, or files.
Can I run Compass without granting the 4 administrative permissions?
Yes, partially. Compass will perform all scanning that relies on read-only permissions. However, features that depend on the 4 administrative permissions (RCD/Copilot settings, Exchange scanning, admin role analysis) will be unavailable or limited. The prerequisite check will flag which features are impacted.
Why does Compass need Sites.FullControl.All if it only reads data?
Sites.FullControl.All is classified by Microsoft as a high-privilege permission because it could be used to modify site collections. Compass only uses it to read the Restricted Content Discoverability (RCD) configuration from the SharePoint Admin REST API, which has no lower-privilege alternative. For all other SharePoint operations, Compass uses Sites.Read.All.
Why does Compass need full_access_as_app for Exchange?
The full_access_as_app EWS permission is needed to scan inbox rules, mail forwarding settings, and mailbox delegations in app-only mode. The Graph API permission Mail.Read cannot access these Exchange-specific configurations. Despite its name, Compass uses this permission strictly in read-only mode.
What is the difference between Compass and a Microsoft 365 security audit?
Cloudiway Compass is an automated AI readiness assessment tool that audits your Microsoft 365 environment for security risks, Copilot readiness, and governance gaps. Unlike manual security audits, Compass scans your entire tenant in minutes and produces an actionable report with risk scores across identity, SharePoint, Exchange, Teams, and compliance areas. Learn more on the product page.
How can I revoke Compass access after an audit?
Go to Microsoft Entra ID → Enterprise applications, find the Compass application, and either remove the admin consent or delete the service principal entirely. This immediately revokes all permissions.
Is Compass compatible with Microsoft 365 Copilot readiness assessments?
Yes. Compass specifically scans Restricted Content Discoverability (RCD) settings, which control what SharePoint content Microsoft 365 Copilot can access. This helps organizations assess and improve their Copilot readiness posture before deployment. See the Copilot Readiness solution for more details.